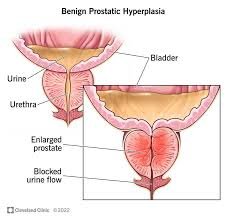
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a disease commonly found in many men as they grow older. It is when the prostate gland becomes enlarged and causes different urinary symptoms. To understand BPH it is important to know about its symptoms, causes and treatment. In this article we will look at the various causes, symptoms, and treatments of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) so you can better understand the condition. Keep reading to learn more.
Anatomy of the Prostate Gland
The prostate gland is a small, walnut shaped gland located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The male reproductive system relies heavily on it since it produces seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm.
Symptoms of BPH
An enlarged prostate can block the flow of urine, due to its pressing against the urethra. This pressure can cause a variety of urinary symptoms, including:
- Frequent Urination: A powerful need to urinate more frequently than usual, particularly at night (nocturia).
- Weak Urine Stream: If you have trouble starting your stream of urine or keeping it going steadily.
- Inability to Empty the Bladder: A sensation of not emptying the bladder after going to the toilet.
- Urgency: The need to urinate quickly can result in an accident.
Causes of BPH
While the exact cause of BPH is not fully understood, several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
- Age: BPH occurs more frequently in older men; by approximately age 50, the risk of the condition greatly increases.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal factors, usually with a rise and fall in testosterone and/or estrogen may also contribute to prostate growth.
- Genetic Factors: The risk for developing BPH is higher if there is a family history of BPH.
Diagnosis of BPH
If you have symptoms of BPH, you should see your healthcare provider. Diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical History: Speaking about any symptoms or medical issues related to this.
- Physical Exam: Urologists can perform a digital rectal exam (DRE) to feel the size of your prostate.
- Urinary Tests: Bladder function tests might include a urine flow study and post void residual volume measurement.
Treatment Options for BPH
Treatment for BPH varies depending on the severity of symptoms and may include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Mild symptoms can be relieved with reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, practicing double voiding and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Medications: Both alpha-blockers and 5 alpha reductase inhibitors can reduce pressure on the muscles around the prostate and the neck of the bladder, and the former can reduce prostate size.
- Surgery: In rare cases, the doctor may remove excess prostate tissue by one of these procedures, such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).
Conclusion
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia is something that happens to a lot of men and could really disrupt your quality of life. Through understanding the causes of the condition, its symptoms and its treatment, one can manage it well. If you do have any urinary difficulty, then it is always best to start first with a urologist in Karachi for an assessment which is more appropriate to how you need to manage it.